[Quality Share] sgRNA Design and Screening
![]()
To achieve efficient gene point mutation and knock-in, it is essential to design sgRNAs with strong cleavage activity and high HDR efficiency.
The design of sgRNAs requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple factors — including the location of candidate editing sites, GC content, and potential off-target risks — to select one or more sgRNAs with high cleavage efficiency and specificity for experimental validation.
The following principles can be used as guidelines for sgRNA design :
01
General Design Principles for Conventional sgRNAs
✅ GC content should preferably not be lower than 40%
✅ Avoid four consecutive T bases within the target sequence
✅ Perform specificity analysis to reduce nonspecific off-target mutations
02
Minimize Distance Between Cleavage Site and Editing Site
To ensure high homologous recombination efficiency, the insertion or point mutation site should be located as close as possible to the sgRNA cleavage site. Existing studies have shown a clear monotonic negative correlation between editing efficiency and distance. In general, the ideal distance is within 10 bp. Beyond this range, recombination efficiency drops significantly.
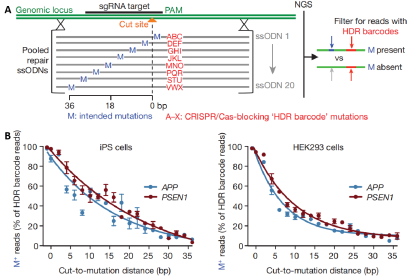
Figure 1. Editing efficiency exhibits a monotonically negative correlation with distance 
03
Design Multiple sgRNAs for Parallel Screening
High theoretical scores do not always guarantee optimal performance in actual cellular experiments.
We recommend initially screening 2–4 candidate sgRNAs in parallel to identify the most efficient one for subsequet experiments.
We recommend initially screening 2–4 candidate sgRNAs in parallel to identify the most efficient one for subsequet experiments.
04
Off-Target Risk Assessment
sgRNA guides the Cas9 enzyme to the target genomic site via base complementarity. However, sequence homology elsewhere in the genome can cause Cas9 to cleave at non-target sites, resulting in off-target effects and undesired mutations.
To minimize off-target risks, the following strategies can be applied:
① Optimize sgRNA Design:
This is the most fundamental step. As the cornerstone of specificity, sgRNAs should be designed using professional software to ensure high genome-wide specific, optimal GC content and avoiding consecutive repetitive sequences.
② Use High-Fidelity Cas9 Variants
Several high-fidelity versions of Cas9 (e.g., SpCas9-HF1, eSpCas9) have been developed. These variants require more precise sgRNA-DNA pairing, significantly reducing mismatch tolerance and effectively mitigating off-target effects.
③ Improve Delivery Methods and Control Expression Duration
Transient delivery methods, such as direct introduction of ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs), rather than using plasmids for sustained expression, can shorten the exposure time of Cas9/sgRNA in cells and lower the chance of unintended cleavage.
④ Apply Comprehensive Off-Target Detection Techniques
Technologies like GUIDE-seq and OGM provide genome-wide off-target assessment, offering a realistic profile of gene editing safety.
Leveraging our proprietary sgRNA design logic, along with advanced synthesis and purification technologies, EDITGENE offers professional sgRNA design and synthesis services to support enterprises and research institutions in efficiently advancing their gene editing projects.












![[Quality Share] sgRNA Design and Screening](/uploads/20250328/ESzk5OC49wpxIHVv_3cbfa5e98ea1d238127fe23c72b0f4b2.png)

Comment (4)